
What is CBG (cannabigerol) and what does this cannabinoid do?
If you’ve spent some time online (like here) or at your local pharmacy, the most popular cannabinoids, THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol), and their effects might seem like old news. But as both the science and legislation surrounding weed research improves, so does our access to the remaining 100+ cannabinoids found in the plant, each with their own unique properties and experiences.
Dubbed a minor cannabinoid as it manifests in trace amounts in most strains, CBG, or cannabigerol, has been around for years and is a worthy addition to your weed encyclopedia and next smoke.
The origins of CBG
Although you may not have heard of CBG, humans have been reaping its benefits in both cannabis and hemp plants for millennia. It was first synthesized alongside THC in 1964 and has been extensively studied for its medicinal potential. It is often referred to as the “mother of all cannabinoids” because without it, cannabis would not have a high.
Do you know the saying that all roads lead to Rome? Well, all cannabinoids trace back to CBG.
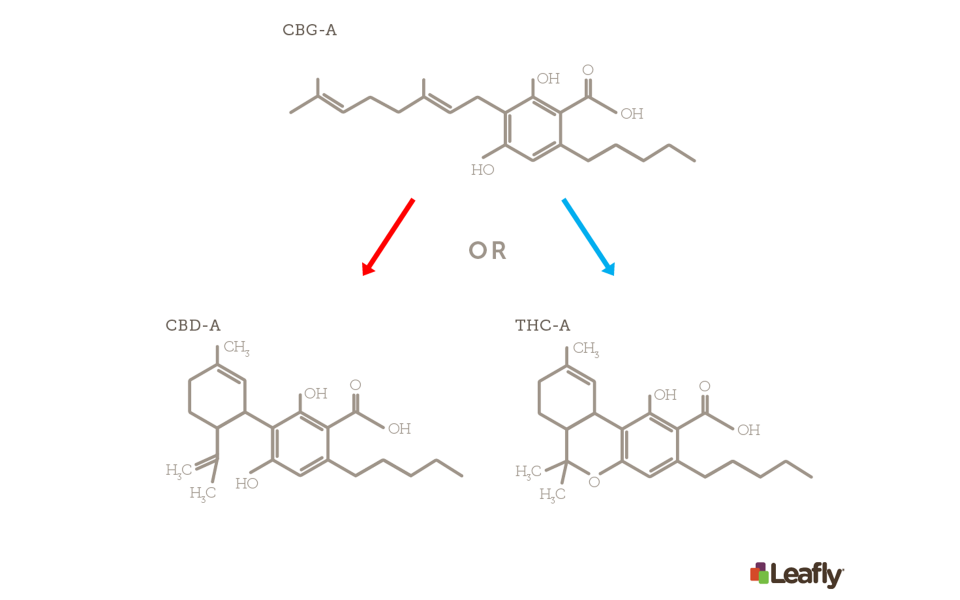
illustration 1: CBG-A is the chemical precursor to THCA, CBDA, and CBCA (not shown). Enzymes in cannabis convert CBGA into either THCA or CBDA, which can then be decarboxylated (“activated”) by light or heat energy to create THC or CBD. (Amy Phung/Leafly)
As young cannabis plants mature and begin to bud, various enzymes and compounds combine to create the precursor to CBG — also known as the “early phase” cannabinoid — called CBGA. At CBGA, all cannabinoids start; As the plant nears the end of its growth cycle and absorbs more and more UV light, CBGA is broken down and converted into THCA and CBDA, the acidic precursors to our two most popular and well-known cannabinoids, THC and CBD. If not bred into, in most cases only a very small amount will become CBG.
CBG in hemp plants
Thanks to the 2018 Farm Bill, hemp plants containing less than 0.3% THC are legal nationwide. CBGA is present in both cannabis and hemp plants, and since it directly correlates to the CBG and CBD potency of the hemp plants, farmers can obtain CBG from hemp plants. In fact, numerous hemp farmers are now breeding and growing CBG-rich strains that don’t require a trip to the dispensary or a medical marijuana card to access.
Since CBG is not abundant in most strains, breeders have started crossing plants to achieve higher concentrations of the cannabinoid. Farms like Oregon CBD have won multiple awards for their White CBG strain, which contains around 10% CBG and less than 0.3% THC.
Related
Hemp puts cows in a mellow mood, science says
Medical Benefits of CBG
Despite its low numbers in mature weed buds, when isolated, CBG shows a number of benefits for the human body.
Like CBD, CBG is non-intoxicating and, despite its association with THC, does not cause a high. Research shows that it can bind to both CB1 and CB2 receptors within the body’s endocannabinoid system, meaning that not only does it interact directly with the body’s internal systems, but it can also counteract the effects of other cannabinoids such as THC .
The human body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS) maintains the body in a balanced state of homeostasis via myriad receptors located in the limbs, organs, nerves, and systems (e.g., digestive, immune, reproductive, and more).
A 2021 patient survey found that the majority of patients found CBG-dominant products to be effective in managing their chronic pain, anxiety, and insomnia, among others.
While there are still gaps in research on CBG, early results suggest that it has numerous health benefits:
- To reduce intraocular pressure and acts as a vasodilator neuroprotectant; This makes it a promising option for treating and managing glaucoma symptoms.
- Anti-inflammatory properties when tested on mice with induced colitis, which could prove to be an effective and holistic treatment for various inflammatory bowel disease.
- combat huntington disease in mice, which causes nerve cell degeneration in the brain by protecting neurons and stopping them from progressing.
- A Agonist for alpha-2 receptors, which are mainly found in the nervous system and regulate blood pressure and heart rate, as well as the activity of the sympathetic nervous system. By inhibiting them, CBG may be able to do this Treat symptoms of Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder.
- High potential as Cancer Inhibitors and Treatmentincluding for breast, gastric and colorectal cancer cells and even glioblastoma brain tumors.
- A antibacterial agent, even against bacterial strains that are resistant to other drugs.
- Appetizing, although studies have only been performed on rats. This may help stimulate appetite in chronically ill patients or those who have lost their appetite due to cancer treatments.
Related
Cancer survivors share the burdens that have helped them move on
Because CBG is non-intoxicating and can be derived from hemp plants, which are federally legal, it is not a planned substance. This means scientists can now access funding to further study the full potential of this particular cannabinoid. The best is yet to come!
Effect differences between CBG and CBD
The recent influx of cannabinoids onto the market means there’s a lot more information to keep track of. At first glance, CBG may seem like a variation of CBD, as both are non-intoxicating and share similar anti-inflammatory properties. But there are key differences that can transform the way you consume them.
CBG and CBD do not bind to the same receptors in the body and are also different at the molecular level. Because CBG can bind to the same receptors as THC, it can potentially address issues affecting the nervous system, including the aforementioned conditions like glaucoma, migraines, muscle soreness, and appetite stimulation.
CBD, on the other hand, may be more effective in immunity-related disorders and in regulating mood disorders.
Both show promise in research for counteracting the effects of THC, and neither will intoxicate the consumer even when taken in high doses.
Related
Does weed help with ADHD?
Weed strains with CBG
Since CBG primarily becomes other cannabinoids, most flowers available from licensed adult dispensaries contain less than 1% CBG.
There are certain strains, such as White CBG, that are bred by hemp farms to produce higher levels of CBG and will not induce a high. Although hemp farmers can legally grow smokable CBG hemp and manufacture CBG products in states that allow it, they are not bound by the same testing standards as cannabis.
Inhaling and ingesting cannabis products with a broad spectrum of cannabinoids and terpenes may have better medicinal and recreational effects than isolated for some individuals – this is referred to as the entourage effect or whole plant medicine. Even if what you consume is not CBG dominant, CBG can still contribute to a pleasurable or therapeutic experience.
We’ve rounded up some of the best high-THC strains that also express CBG:
CBG products are popping up more and more in the adult, medical marijuana, and hemp markets as this cannabinoid continues to prove its worth trying.
Read more about cannabinoids
Amelia Williams
New York-based freelance cannabis journalist Amelia Williams is a graduate of San Francisco State University’s journalism program and a former budtender. Williams has contributed to GreenState, MG Magazine, Culture Magazine and Cannabis Now, Kirkus Reviews and The Bold Italic of the San Francisco Chronicle.
Check out Amelia Williams’ articles
By submitting this form, you are subscribing to Leafly news and promotional emails and agreeing to Leafly’s Terms of Service and Privacy Policy. You can unsubscribe from Leafly email communications at any time.

Post a comment: